*) Gambar sebagai ilustrasi
Let’s analyze the Four Types of Innovation diagram systematically using your PRODUCT Framework (Perceive → Refine → Organize → Develop → Understand → Calibrate → Transfer) as a design guide for building a system based on it.
Analysis of Four Types of Innovation (via PRODUCT Framework)
1. Perceive the Need
- Observed Need: Organizations face complexity in managing different types of innovation (Product, Process, Business Model, Management).
- Pain Points:
- Innovation efforts are often fragmented.
- No integrated platform to map and monitor different innovation types.
- Strategic vs. operational innovations are rarely balanced.
- Need Statement: A system that helps organizations identify, categorize, and manage innovations systematically across all four quadrants.
2. Refine the Idea
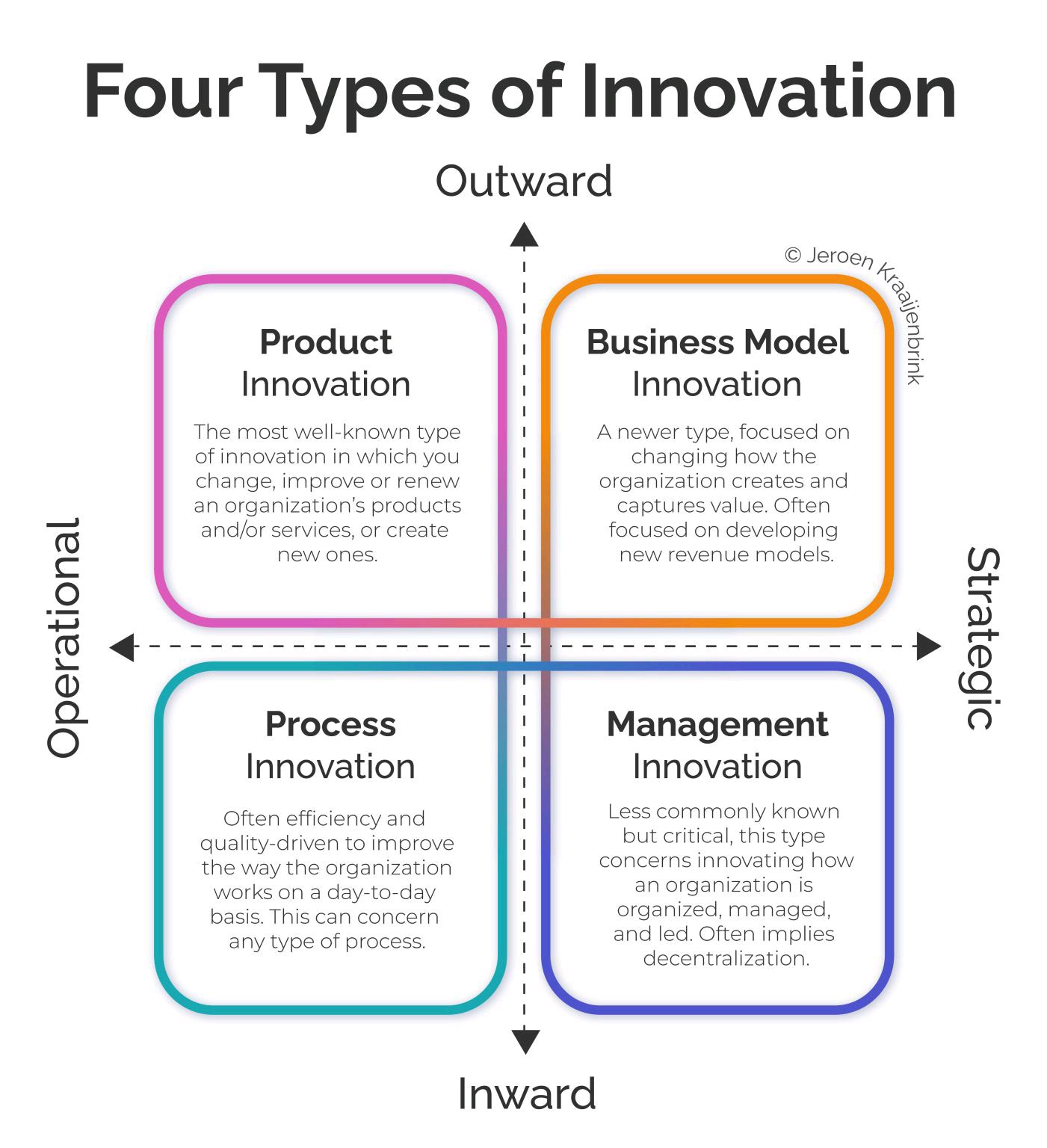
- Core Concept: Build an Innovation Management System that categorizes activities into:
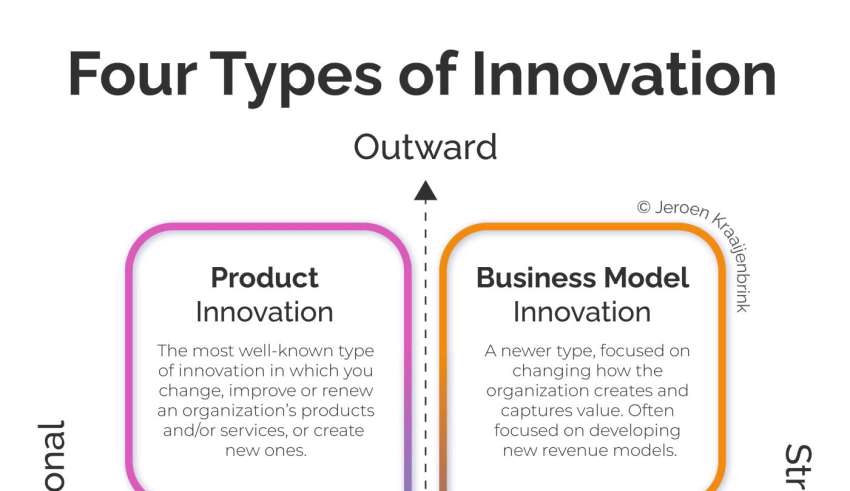
- Product Innovation (new products/services).
- Process Innovation (efficiency, quality).
- Business Model Innovation (revenue models, value creation).
- Management Innovation (organizational design & leadership).
- Refinements:
- Add metrics (operational vs. strategic, inward vs. outward).
- Enable dynamic mapping of projects into quadrants.
- Provide analytics dashboards for innovation portfolios.
3. Organize the Process
- System Architecture Planning:
- Modules:
- Innovation Idea Submission.
- Categorization Engine (classifies into 4 types).
- Workflow Management (approval, testing, scaling).
- Knowledge Repository (captures insights).
- Dashboard & Analytics (measures innovation balance).
- Data Flow:
- Users submit ideas → categorized → linked to knowledge assets → tracked through lifecycle.
- Stakeholders: Managers, employees, R&D teams, executives.
- Modules:
4. Develop the Prototype
- Prototype Features:
- Quadrant visualization (Product, Process, Business Model, Management).
- Input form for innovation ideas.
- Simple workflow: draft → review → pilot → approved.
- Dashboard showing ratio of operational vs. strategic projects.
- Technology Stack (example):
- Web platform (React/Angular frontend).
- Backend with database (PostgreSQL, MongoDB).
- Integration with KM tools (Confluence, SharePoint).
5. Understand the Feedback
- Feedback Sources:
- Users: Ease of categorizing innovation ideas.
- Managers: Clarity in monitoring innovation portfolios.
- Executives: Usefulness of analytics in strategic decisions.
- Expected Insights:
- Some innovation types might be over/underrepresented.
- Users may need clearer guidelines to classify innovations.
6. Calibrate & Iterate
- Improvements:
- Enhance categorization with AI (NLP to classify ideas automatically).
- Refine dashboards to track ROI and innovation impact.
- Add collaboration features (comments, voting, mentorship).
- Iteration Cycle: Agile sprints with user testing every 2–3 weeks.
7. Transfer to Market
- Deployment Strategy:
- Start with internal company adoption (HR + R&D).
- Scale to industry networks (innovation ecosystems).
- Offer SaaS model for SMEs and enterprises.
- Knowledge Capture: Lessons from early adopters → improve version 2.0.
- Impact: A knowledge-driven innovation management system aligning product, process, business model, and management innovations.
Conclusion
By applying the PRODUCT Framework:
- The Need is identified → fragmented innovation management.
- The Idea is refined into a structured system.
- The Process organizes workflows, data, and stakeholders.
- The Prototype makes the 4-quadrant model interactive.
- Feedback validates usability and impact.
- Iteration improves accuracy and user adoption.
- Transfer ensures scalability as a commercial/organizational tool.
Thus, this framework enables you to design a systematic Innovation Management Platform that transforms the static 2×2 diagram into a dynamic, actionable ecosystem.
If you have questions regarding training, mentoring, the analysis of Framework implementation, and the development of systems that we provide, and wish to collaborate, please contact us via haitan.rachman@inosi.co.id.







